Neuropharmacology: Targeted Drug Delivery for Neurological Disorders

In the world of healthcare, targeted neuropharmacology is a new hope for fighting neurological disorders. It combines pharmacology, neuroscience, and molecular biology. This field aims to create drugs that hit the right spot in the brain.
Getting drugs past the blood-brain barrier is a big challenge. But, new tech like nanotechnology and biomarkers are changing the game. They could lead to treatments tailored for Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis.

The study of neurological disorders is always moving forward. It’s all about finding the right treatments through precision medicine and advanced molecular neuroscience. By studying the brain’s inner workings, scientists are making drugs that really work.
Next, we’ll dive into the basics of neuropharmacology. We’ll look at the latest in drug delivery and how these new methods are being used in real-world treatments. Let’s explore how this field is changing the game for people with neurological diseases.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Neuropharmacology
Neuropharmacology is a key area in medicine that studies how drugs affect the brain. It focuses on drug-brain interactions. It also deals with the blood-brain barrier and neurotransmitters, which are vital for brain signals and treatments.
Basic Principles of Drug-Brain Interaction
The brain is the body’s control center and is very complex. Drugs must find their way through this complex system to work. Drug-brain interaction affects how well drugs work and their side effects.
Blood-Brain Barrier Challenges
The blood-brain barrier is a big challenge in neuropharmacology. It’s a protective layer that keeps many substances out of the brain. Researchers must find ways to get drugs past this barrier to treat the brain effectively.
Neurotransmitter Systems
Neurotransmitters are key for brain signals. Neurotransmitter modulation is important in neuropharmacology. It helps in understanding and treating neurological disorders. Knowing about synaptic plasticity is also crucial for creating effective treatments.
Studying neuropharmacology opens up new ways to treat neurological diseases. It helps in creating better treatments and improving patient care.
| Key Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Drug-Brain Interaction | The absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination of pharmaceutical agents within the brain, influencing therapeutic efficacy and side effects. |
| Blood-Brain Barrier | A highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents many substances from reaching the brain, posing a significant challenge in drug delivery. |
| Neurotransmitter Modulation | The regulation of chemical messengers in the nervous system, essential for managing neurological disorders associated with neurotransmitter imbalances. |
| Synaptic Plasticity | The ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, a crucial concept in developing effective targeted therapies. |
The Evolution of Targeted Drug Delivery Systems
The field of targeted drug delivery has seen big changes. It’s moving from old ways to new, precise methods. This change comes from understanding brain disorders better and the need for treatments that fit each person.
Nanocarrier technologies are a big step forward. These tiny vehicles, like liposomes and nanoparticles, carry drugs right to the brain. They make drugs work better and last longer by protecting them.
Smart polymers are also important. These materials change shape in response to their environment. This means they can release drugs exactly where they’re needed.
Receptor-mediated transport is another key area. It uses the brain’s own transport systems to get drugs past the blood-brain barrier. This is a big challenge in delivering drugs to the brain.
Today, drug delivery is more about treating each person as an individual. Thanks to new ways of diagnosing and understanding genes, drugs can be made just for you. This makes treatments more effective and safer.
The future of targeted drug delivery looks bright. It promises better treatments for many brain diseases. As these technologies get better, people with these conditions will have more hope for a better life.
Targeted Neuropharmacology for Neurological Disorders: Current Approaches
In the field of targeted neuropharmacology, new methods are being developed. These aim to get drugs to the right places in the brain more effectively. We’ll look at three key strategies: Nanocarrier Technologies, Smart Drug Delivery Platforms, and Receptor-Mediated Transport.
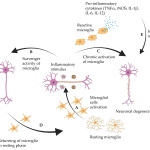 The Role of Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases
The Role of Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Nanocarrier Technologies
Nanocarriers like liposomes and nanoparticles are showing great promise. They can carry drugs into the brain, protecting them from being broken down. By targeting specific areas, they help drugs work better and reduce side effects.
Smart Drug Delivery Platforms
Smart drug delivery uses materials that change in response to their environment. This ensures drugs are released where and when needed. It’s a way to make treatments more effective and safer.
Receptor-Mediated Transport
This method uses brain cells’ receptors to get drugs into the brain. By attaching drugs to molecules that bind to these receptors, they can cross the blood-brain barrier. It’s a clever way to get drugs to where they’re needed most.
These new approaches in neuropharmacology, along with Precision Medicine, are very promising. They help doctors tailor treatments for better results and fewer side effects. This could lead to more effective treatments for neurological conditions.
Molecular Mechanisms of Neural Drug Targeting
Exploring Molecular Neuroscience is key to understanding Neural Drug Targeting and its effects on Synaptic Plasticity. It helps us see how drugs work at a cellular and molecular level. This includes how they interact with receptors, trigger signals, and change how synapses work.
Tools like optogenetics and chemogenetics have given us new insights. They let us control and watch neurons closely. This helps scientists understand how drugs affect brain circuits and help with neurological issues.
Studying these mechanisms is very important. It helps researchers make better neurotherapeutics. This means treatments that are more precise and effective for different neurological problems.
| Molecular Mechanism | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Receptor-Ligand Interactions | Exploring the specific binding of drug molecules to neuronal receptors and the downstream signaling cascades they trigger. |
| Signal Transduction Pathways | Investigating the complex intracellular signaling networks that mediate the effects of drugs on neuronal function and plasticity. |
| Synaptic Plasticity | Analyzing the impact of drugs on the dynamic changes in the strength and structure of synaptic connections, which underlie learning, memory, and neurological processes. |
By studying these molecular mechanisms, researchers can unlock the full potential of Neural Drug Targeting. This opens the door to more effective and personalized treatments for many neurological disorders.
Biomarker-Guided Treatment Strategies
In the field of neurological disorders, new ways of treating patients have emerged. These methods use genetic, protein, and imaging biomarkers. This allows doctors to tailor treatments to each patient, leading to better results and more effective care.
Genetic Biomarkers
Genetic biomarkers are key in Biomarker-Guided Treatment. They help find out who will benefit from certain treatments. This way, doctors can make better choices. Thanks to Neurogenomics, scientists can find genetic factors that affect how well drugs work, helping in Translational Neuropharmacology.
Protein-Based Markers
Protein biomarkers give insights into how diseases progress and how well treatments work. By watching protein levels, doctors can understand a patient’s condition better. This helps them adjust treatments for better results. These markers are vital in treating neurological disorders.
Imaging Biomarkers
New imaging tech like PET and MRI scans has led to imaging biomarkers. These biomarkers show what’s happening in the brain and how drugs affect it. With Biomarker-Guided Treatment, doctors can make better choices, improve treatment plans, and track disease progress.
Using genetic, protein, and imaging biomarkers in Biomarker-Guided Treatment is crucial for personalized medicine in neurology. These new methods promise better patient care, lower costs, and more effective treatment of neurological disorders.
| Biomarker Type | Application in Neurological Disorders | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Biomarkers | Identifying patient-specific genetic variants that influence drug response | Enables personalized treatment selection, improved outcomes, and enhanced Translational Neuropharmacology |
| Protein-Based Markers | Monitoring disease progression and treatment efficacy | Provides valuable insights for adjusting treatment strategies and optimizing Biomarker-Guided Treatment |
| Imaging Biomarkers | Visualizing brain function and drug effects | Enhances decision-making, treatment planning, and monitoring of neurological conditions |
Advanced Drug Delivery Technologies
Researchers are working on new Advanced Drug Delivery methods. They aim to get drugs past the blood-brain barrier. This is to help treat complex brain disorders by targeting specific areas of the brain.
Convection-enhanced delivery (CED) is one such method. It uses pressure to get drugs into the brain. This is good for drugs that are hard to get past the blood-brain barrier.
Focused ultrasound-mediated drug delivery is another approach. It uses sound waves to open up the blood-brain barrier. This lets drugs get into the brain more easily.
Intranasal delivery systems are also being explored. They send drugs up the nose to the brain. This way, drugs can avoid the blood-brain barrier and work better on the brain.
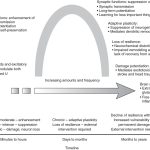 How does chronic stress affect the functioning of the hippocampus?
How does chronic stress affect the functioning of the hippocampus?
New technologies include gene therapy and using engineered cells to carry drugs. These methods can target specific brain areas. They promise more effective treatments for many brain disorders.
These advanced drug delivery methods are changing how we treat brain diseases. They could lead to better treatments and improve life for those with neurological conditions.
| Advanced Drug Delivery Technology | Key Characteristics | Potential Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Convection-Enhanced Delivery (CED) | Utilizes a pressure gradient to bypass the blood-brain barrier and directly infuse drugs into targeted brain regions. | Delivery of large-molecule therapeutics, such as proteins and gene therapies, for the treatment of neurological disorders. |
| Focused Ultrasound-Mediated Drug Delivery | Uses focused ultrasound waves to temporarily disrupt the blood-brain barrier, allowing for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents. | Delivery of small-molecule drugs and biologics for various neurological conditions. |
| Intranasal Delivery Systems | Administers drugs through the nasal route, bypassing the blood-brain barrier and directly targeting the central nervous system. | Enhancement of therapeutic efficacy for certain neurological treatments. |
| Gene Therapy Approaches | Utilizes genetic material to target and modulate specific neurological pathways. | Personalized treatments for a wide range of neurological disorders. |
| Engineered Cells as Drug Delivery Vehicles | Uses genetically modified cells as carriers to deliver therapeutic agents to targeted brain regions. | Precise targeting and modulation of neurological pathways for improved therapeutic outcomes. |
Personalized Medicine in Neurological Treatment
Personalized medicine is changing how we treat neurological disorders. It makes treatments fit each patient’s needs. This way, treatments work better and are safer.
Patient-Specific Drug Design
Patient-specific drug design is key to personalized medicine. It considers a patient’s genes, age, and disease stage. This helps create treatments that are just right for them.
Doctors can see how a patient’s genes affect how they react to drugs. This lets them make treatments that work better and have fewer side effects.
Genomic Profiling Applications
Genomic profiling is a big help in making personalized treatments. It looks at a patient’s genetic information. This helps doctors understand the disease better and make treatments that fit each patient.
Big data and artificial intelligence are making personalized treatments even better. They help doctors use lots of data to make smarter choices. This technology is making treatments more effective and safer for patients.
Neuroprotective Strategies and Drug Delivery
In the fight against neurological disorders, finding ways to protect the brain is key. These new methods aim to keep brain function strong and stop further harm. They offer hope to those suffering from serious conditions.
Antioxidant therapies are one such strategy. They target oxidative stress, which can harm brain cells. Anti-inflammatory treatments also play a role, reducing inflammation that damages the brain.
Another promising area is the delivery of neurotrophic factors. These important molecules help grow and keep brain cells healthy. They make brain cells stronger against disease.
Improvements in drug delivery systems have also been crucial. Targeted neuropharmacology uses new technologies like nanocarriers. These ensure drugs are released exactly where needed in the brain. This approach boosts treatment effectiveness while reducing side effects.
By combining these strategies with advanced drug delivery methods, researchers are making progress. This work, based on synaptic plasticity and understanding brain mechanisms, offers hope. It aims to improve life for those with neurological disorders.
Clinical Applications in Major Neurological Disorders
Targeted neuropharmacology is being explored for major neurological conditions. This offers hope for better patient outcomes and quality of life. In Alzheimer’s disease, researchers are working on clearing amyloid-beta and targeting tau protein.
Parkinson’s disease therapies aim to replenish dopamine and protect neurons. This addresses the motor and non-motor symptoms of the disease. For multiple sclerosis, management involves immunomodulation and remyelination, using the latest in drug delivery.
Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment
Targeted drug delivery systems are being developed for Alzheimer’s. They aim to clear amyloid-beta and inhibit tau protein aggregation. These approaches hope to slow cognitive decline and improve life quality for Alzheimer’s patients.
Parkinson’s Disease Therapy
Parkinson’s disease management has seen big advancements. Strategies now focus on replenishing dopamine to address motor symptoms. They also aim to protect dopaminergic neurons.
These targeted therapies aim to improve both physical and cognitive aspects of Parkinson’s. They aim to enhance the overall well-being of patients.
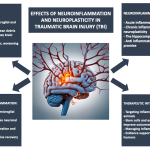 Neuroplasticity and Cognitive Recovery After Traumatic Brain Injury
Neuroplasticity and Cognitive Recovery After Traumatic Brain Injury
Multiple Sclerosis Management
In multiple sclerosis, targeted drug delivery systems are used to modulate the immune system and promote remyelination. These systems aim to target immune dysregulation and regenerate myelin sheaths.
Improved treatment outcomes and reduced side effects are the goals. These targeted therapeutic strategies hold promise for managing relapsing-remitting and progressive forms of the disease.






